-
30
Jan
Background noise and spike overlap pose problems in contemporary spike-sorting strategies. The (non-linear) isometric feature mapping (ISOMAP) technique reveals the intrinsic data structure and helps with recognising the involved neurons.
To reproduce this tutorial in MATLAB you will need :
1. ISOMAP source code for MATLAB (for more information and updated version see here: http://isomap.stanford.edu)
2. Memo script for MATLAB and sample data to reproduce the results shown below.
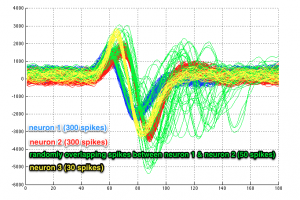
In this tutorial we will use simulated spikes from 3 neurons, one being a sparsely-firing one.
Let us take a look at the data set first:
- 300 spikes for neuron no.1 (lines 1-300)
- 300 spikes for neuron no.2 (lines 301-600)
- 50 randomly overlapping spikes between neurons no.1 and no.2 (lines 601-650) – to make things more challenging
- 30 spikes for neuron no.3 (lines 651-680)
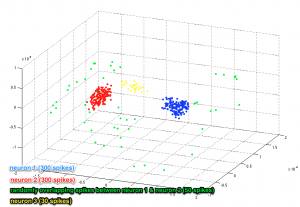
Apply ISOMAP algorithm
D = L2_distance(spikes’,spikes’,1);
[Y, R] = IsomapII(D, ‘k’, 200, options);
Notes
- Changing the ‘k’ value will affect the output of the algorithm, i.e. projecting the data in ISOMAP space. For details see [1]
- Projection coordinates are kept in ‘Y’. ‘R’ denotes residual variance.
For more details see [1]
If you find this tutorial useful, please cite:
[1] Adamos DA, Laskaris NA, Kosmidis EK, Theophilidis G. “NASS: an empirical approach to spike sorting with overlap resolution based on a hybrid noise-assisted methodology“. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 2010, vol. 190(1), pp.129-142. | http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2010.04.018
For more information see: http://neurobot.bio.auth.gr/spike-sorting/
(C) D.A. Adamos, 2010.
- Published by Dimitrios A. Adamos in: Software Tutorials
- RSS feed subscription!

 Neurobot via RSS
Neurobot via RSS
